What Is Sodiceram and Why It Matters? Complete Guide (2026)

Sodiceram is emerging as one of the most advanced innovations in modern ceramic technology. Unlike traditional ceramics that focus mainly on durability or appearance, Sodiceram’s combines material science, sustainability, and design flexibility in one solution. As industries move toward stronger, longer-lasting, and eco-friendly materials, sodiceram is gaining attention across construction, architecture, interior design, and industrial applications.
In 2026, the demand for high-performance ceramic materials is higher than ever. Sodiceram stands out because it offers low porosity, high strength, excellent thermal resistance, and long service life without compromising aesthetics. Whether you are a homeowner, architect, engineer, or simply curious about next-generation materials, understanding Sodiceram’s can help you make smarter and future-ready choices.
This guide explains Sodiceram’s in simple language, covers its real-world uses, benefits, limitations, cost, and future trends, and helps you decide whether it is the right material for your needs.
What Is Sodiceram and Why It Matters Today
Sodiceram is a modern ceramic material developed using sodium-based compounds to improve the internal structure of traditional ceramics. The word “sodiceram” comes from two parts: sodium and ceramic. Sodium plays a key role during the firing process by acting as a flux, which helps the ceramic body become denser and less porous.
What makes Sodiceram’s important today is its ability to solve common problems found in regular ceramics. Traditional ceramic tiles and surfaces often absorb moisture, crack under thermal stress, or wear out over time. Sodiceram’s reduces these issues by creating a tighter, more compact structure that resists water, chemicals, and temperature changes.
In a world where durability, sustainability, and long-term value matter more than ever, Sodiceram’s offers a practical alternative to porcelain, natural stone, and even engineered materials.
How Sodiceram’s Is Different From Traditional Ceramics
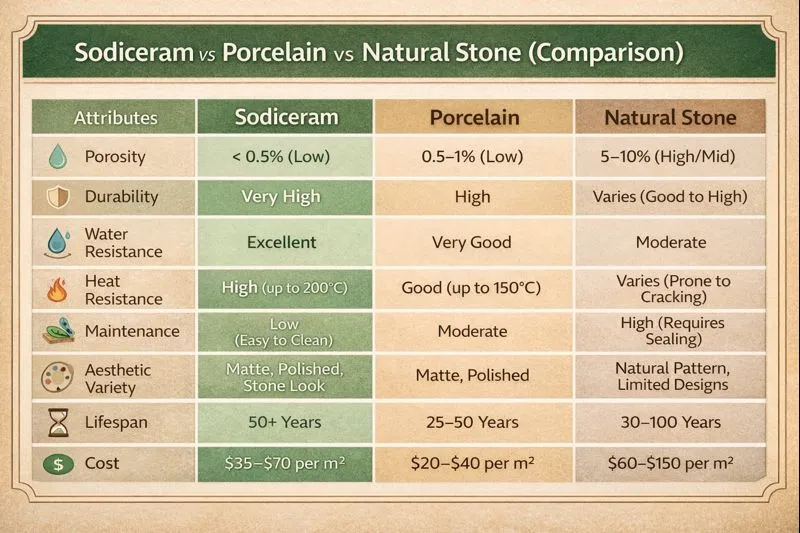
The main difference between Sodiceram’s and traditional ceramics lies in its internal composition and performance. Standard ceramics usually rely on clay, quartz, and feldspar, which can leave microscopic pores after firing. These pores allow water absorption and weaken the material over time.
Sodiceram uses sodium-infused compounds that improve vitrification during firing. This results in:
- Much lower porosity
- Higher density
- Better resistance to moisture and stains
- Improved strength and durability
Another key difference is consistency. Traditional ceramics may vary in quality depending on firing conditions, while sodiceram is produced with controlled formulations and advanced processing. This makes sodiceram more reliable for demanding environments such as commercial buildings, laboratories, and outdoor installations.
From a design perspective, sodiceram also supports a wider range of finishes, including matte, polished, stone-look, and marble-style surfaces, without sacrificing strength.
Key Material Science Behind Sodiceram’s (Explained Simply)
At its core, sodiceram is based on smart ceramic chemistry. Sodium compounds lower the melting point of silica during firing, allowing the ceramic particles to bond more closely together. This process fills micro-gaps inside the material and creates a strong glass-like phase that holds everything tightly in place.
Because of this structure, sodiceram achieves:
- Very low water absorption
- Higher mechanical strength
- Better resistance to thermal shock
- Longer lifespan compared to standard ceramics
In simple terms, sodiceram is engineered to be tougher on the inside while still looking refined on the outside. This balance of science and design is what makes it suitable for both technical and decorative applications.